Cloud hosting quickly becomes the preferred choice for businesses looking to leverage technological advancements and maximize efficiency.
You’ve heard about public and private clouds.
But how about Hybrid cloud hosting?
Hybrid cloud hosting is a unique type of cloud hosting that combines the strengths of public cloud services with private cloud capabilities.
This type of hosting provides organizations with increased flexibility, scalability, redundancy, and cost savings.
It can also provide greater control over data security and privacy than relying solely on public clouds.
This article will discuss hybrid cloud hosting and how it works in detail.
What is hybrid cloud hosting?
As its name suggests, hybrid cloud hosting is actually a combination of both public and private cloud computing solutions.
It combines the best features of both worlds to maximize performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
With hybrid hosting, you can enjoy the benefits of a public cloud, such as lower costs and greater flexibility, while also taking advantage of the security benefits of private clouds.
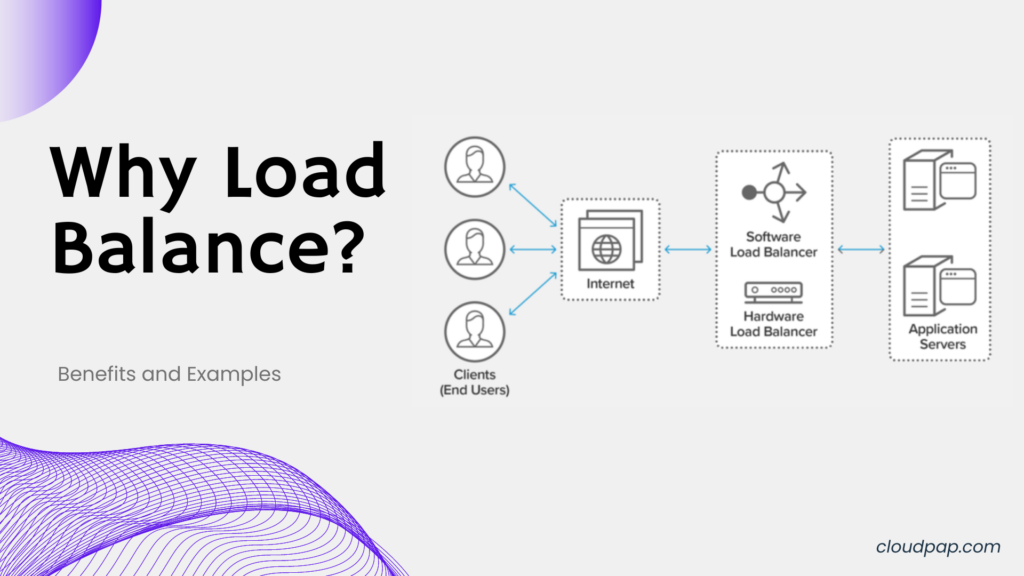
Here’s how it works
The public cloud portion provides access to shared resources such as storage, computing power, and network connections through an on-demand model.
This means you can quickly scale up or down depending on your current needs without investing in more hardware or software.
The private cloud part is dedicated solely to an organization’s use and offers higher levels of security than what would be available on a public infrastructure.
It’s that simple.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Hosting
Being the ‘child’ of both public and private cloud?, the hybrid comes with some perks.
a. Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance is actually the ability of a system to continue functioning properly in the event of failure or disruption of one or more components.
And boy?, Hybrid cloud hosting offers greater levels of resilience.
How?
Well, it combines public and private clouds, leveraging their respective strengths to ensure optimal uptime and performance across the entire infrastructure.
For example, suppose a component fails on the public cloud side, such as an application server running in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) public cloud.
In that case, redundancy is still available through its counterpart running on a private cloud hosted on-premises.
The result is increased reliability and availability since hybrid clouds allow organizations to draw from multiple sources without suffering any downtime or disruption.
b. Scalability
In itself, scalability means the ability to increase or decrease the capacity of a system quickly, often depending on current demand levels.
This makes hybrid cloud hosting attractive because it allows businesses to scale up or down as needed easily without having to invest in additional software or hardware.
You also benefit from more flexibility when it comes to your computing needs.
c. Cost Savings
When it comes to cost savings, hybrid cloud hosting is the perfect solution for many businesses.
Considering it combines private and public clouds, organizations can scale their infrastructure as needed without investing in additional hardware or software licenses.
You no longer need to pay for an extra layer of security or manage separate networks for each cloud provider since all services are connected together through the hybrid network.
And if you have fluctuating usage needs, hybrid cloud hosting can also be a great way to save money on resources that are not used regularly.
You can quickly increase or decrease computing power depending on the workloads you’re running at any given time.
This comes in handy when working with data-intensive applications such as video streaming or analytics, where there may be considerable spikes in resource utilization throughout the day.
d. Security
Hybrid cloud hosting provides both private and public servers that allow for secure access to critical data, applications, and workloads.
Considering private servers are located on-premise or in an organization’s own data centre, they provide a trusted environment that can be tailored to the company’s specific requirements.
On the other hand, public servers exist in the cloud, allowing the organization access to additional resources such as storage space and compute power.
Now, when you combine multiple layers of security with both types of servers, organizations can keep their sensitive information safe from unauthorized access or malicious attacks.
One more thing.
Hybrid cloud hosting also allows companies to control their own level of risk management with customizable policies to meet their compliance requirements.
You have control over user authentication methods as well as where and how they store data within the cloud environment.
Types of Hybrid Cloud Architectures
One type of hybrid cloud architecture is called multi-cloud, where multiple providers host different components.
This allows companies to take advantage of each provider’s different products without investing in additional hardware or software licenses.
They can also use different providers for different aspects of their operations such as storage, networking, and compute resources.
Another common type of hybrid cloud architecture is known as “federated” or “containerized” clouds.
In this architecture, a customer would use multiple cloud providers for distinct services such as security or development.
The customer also uses an orchestration platform to manage the different services from different providers.
What is the best example of a hybrid cloud?
The best example of a hybrid cloud is one that leverages a combination of private and public clouds to achieve the most cost-effective, secure solution.
Organizations can mix and match different aspects of their IT infrastructure, such as on-premise servers, storage devices, and virtual private networks, with various cloud offerings from Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
This approach allows them to maintain control over certain portions of their environment while still taking advantage of the scalability, flexibility, and cost savings available from the public cloud.
For example, they can keep highly sensitive data behind their own firewall while moving less critical applications out into the public cloud.
Which are the most common uses of hybrid cloud?
The most common uses of hybrid cloud are for organizations that need to store sensitive data in a secure environment but also want the flexibility and scalability of the public cloud.
Hybrid cloud allows businesses to leverage private and public cloud resources, benefiting from the best of both worlds.
Another common use case for hybrid cloud is disaster recovery. With hybrid cloud, businesses can back up their data in a secure private cloud environment while also having access to the scalability and reliability of a public cloud.
This allows them to quickly recover from any outages or disasters without having to worry about data loss or downtime.
Finally, hybrid cloud is often used by businesses that need to scale their applications quickly and easily.
By leveraging private and public clouds, they can quickly add more resources as needed without investing in additional infrastructure or hardware.
This makes it easy for businesses to scale their applications on demand while still keeping costs down.
Related: